Vision & Mission / Programs
Aimtron Foundation is a “platform” to give back to Society. Together we can reach many more, do join hands with us, in this endeavor.
VISION – Enrich Society Gratefully
MISSION – Adopt technology pragmatically as a catalyst to enhance society’s ‘Skill, Knowledge, and self worth’ through relevant and sustainable activities.
VALUES –
- Respect – Advance a culture of Mutual respect
- Courteous – Demonstrate the spirit of “Service with dignity”
- Humility – Serve with Modesty.
Programs
- Outreach programs
- Internships
- Webinars
- Soft skills Workshops
- Centre of Excellence
- Provide Global Reach
- Incubation centers
- Think tank
- Mentorship programs
- Entrepreneurial Coaching / Networking opportunities
- Community Health awareness camps
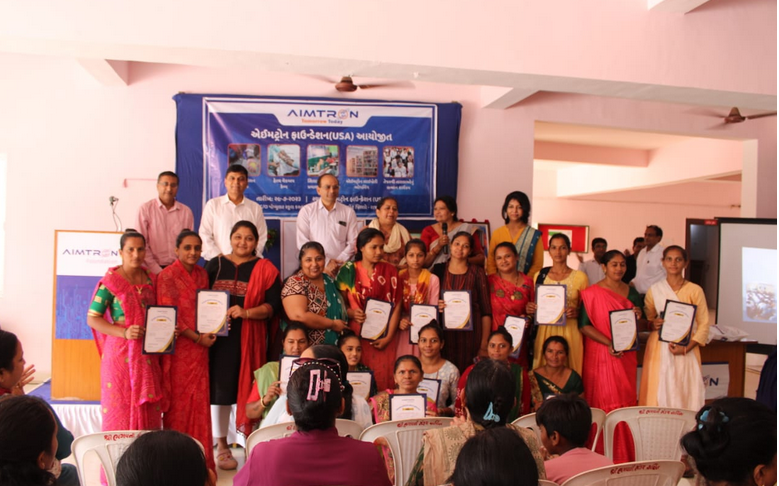
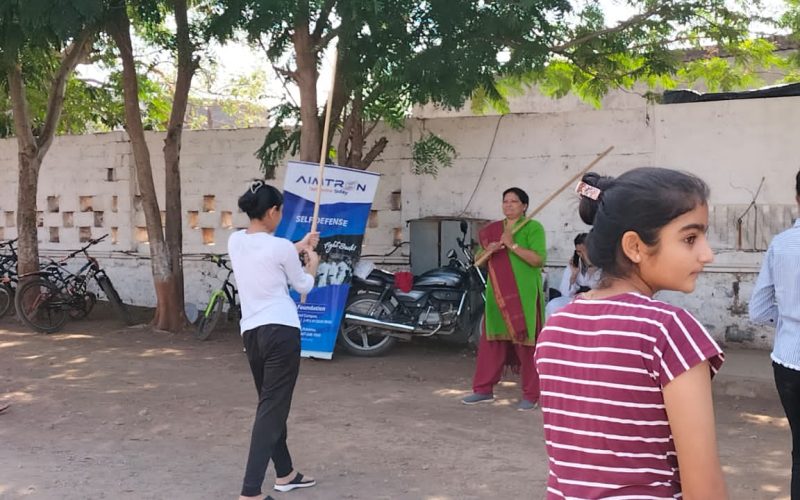
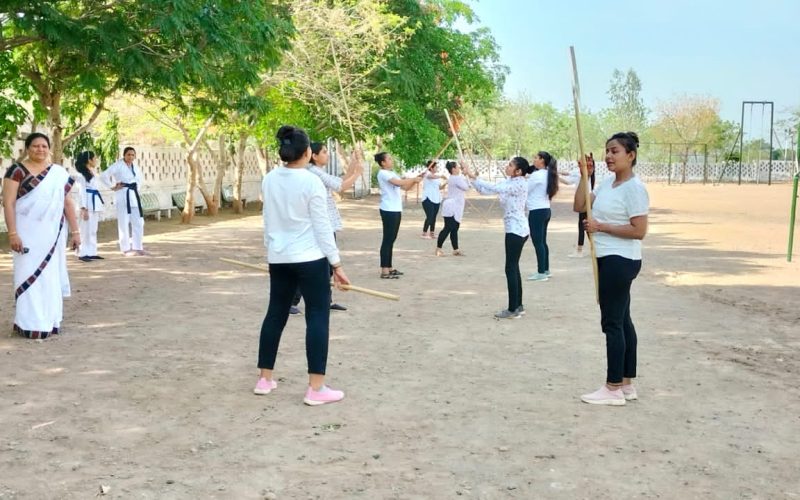
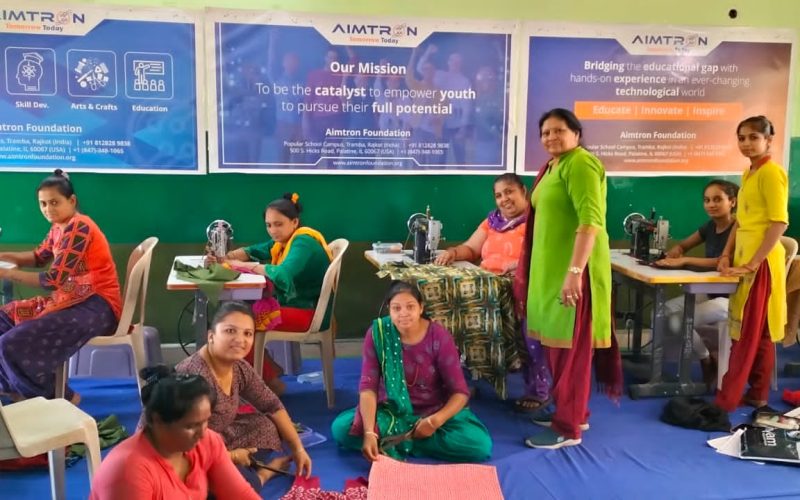
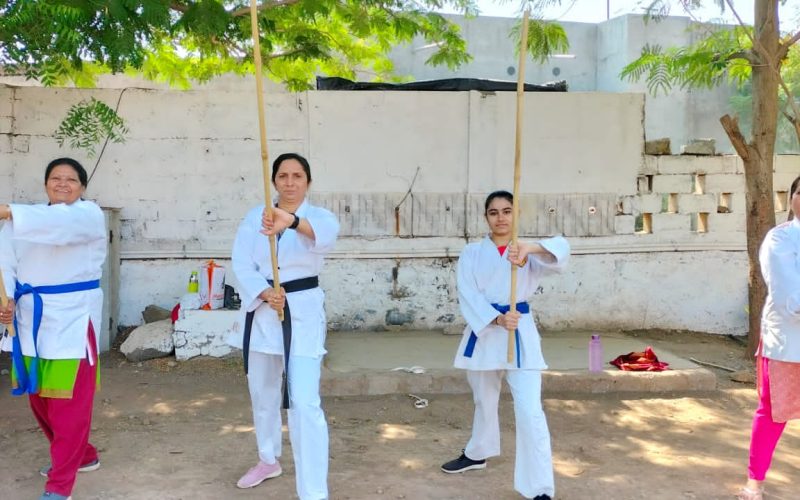
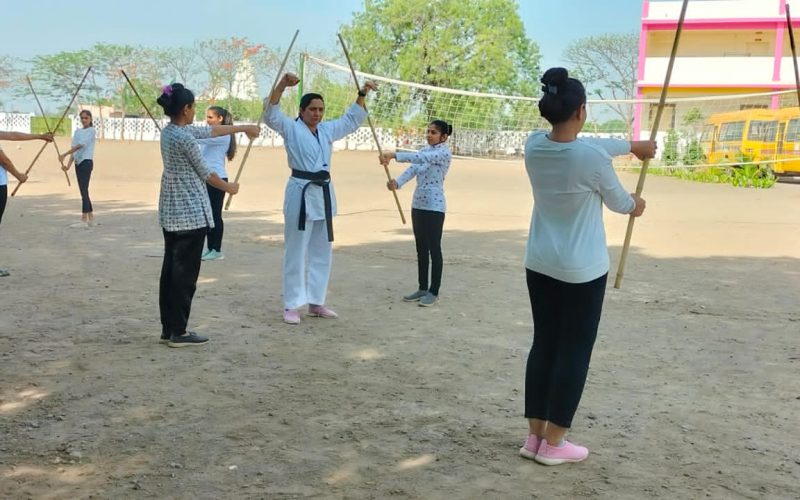
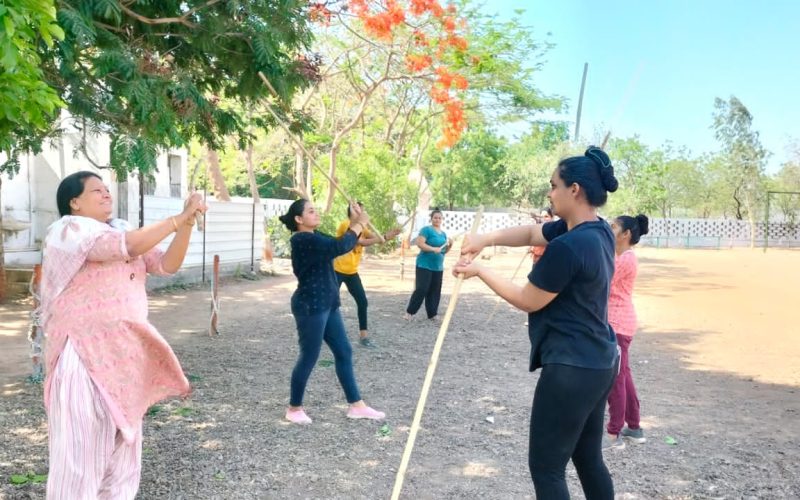
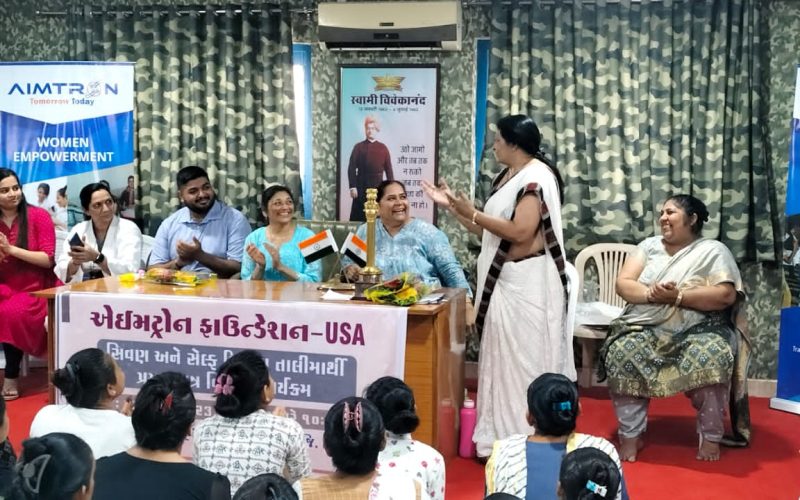
- Women Empowerment
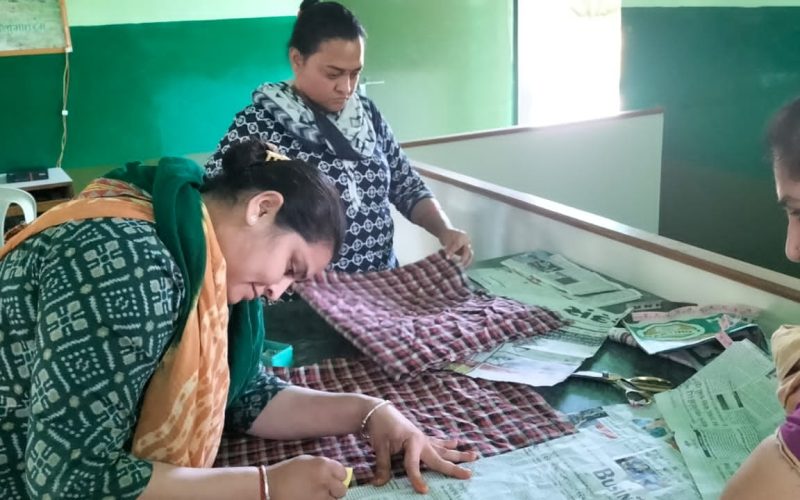
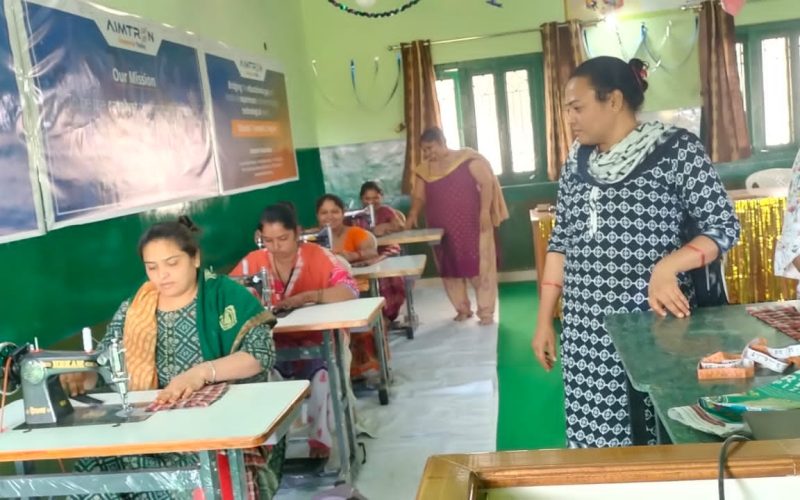
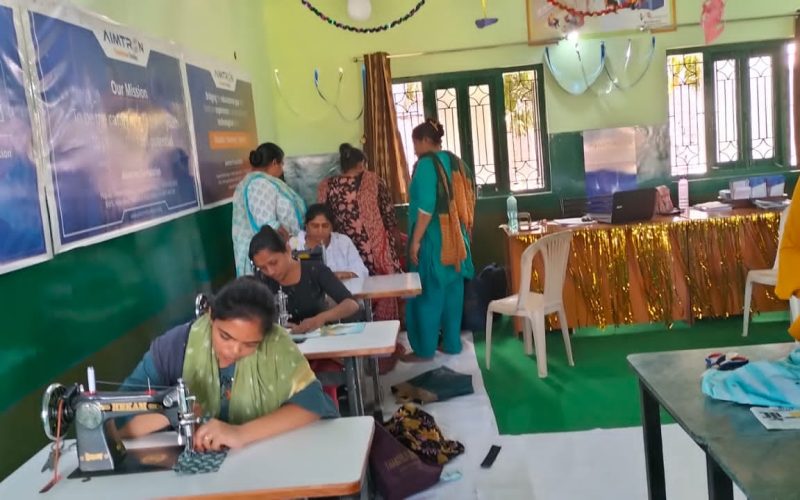
- Vocational trainings for ladies
- Tailoring Courses
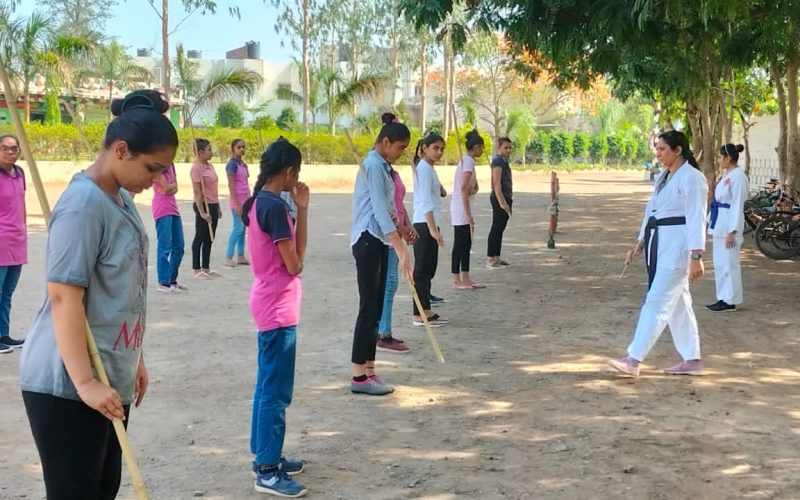
- Self Défense workshops
- Computer courses
- Spoken English
Aimtron Foundation aspires to create exposure and awareness to attract youth and non-traditional candidates to manufacturing careers. Create an industry-endorsed process for interns and apprentices to address the challenges between academia and industry, through tours, webinars and programs, designed to educate, inspire, and prepare youths to pursue career in technology and manufacturing. Appreciating the need for creation of large reservoir of highly qualified youths.
INTEND to form a nucleus for promoting excellent quality youths in the fields of engineering and technology. Our mission is to be the catalyst to empower youth to pursue their full potential.
Scholarship & Mentorship Program
The Aimtron Foundation Scholarship program is a financial assistance program to support students who has well defined academic goals to pursue their further studies. The program aims to bridge the gap between financial constraints and academic aspirations, and to empower students to achieve their full potential. Students whose annual family income is below INR 3 lakhs are eligible for this Orphans or Single Parent Child Scholarship program. Every year 3 deserving students will be granted scholarships.
About the Program:
• Eligibility : The scholarship applies to students who are orphans or single parent child.
• Financial assistance: The scholarship provides financial aid of up to INR 1 Lakh per year (as per the course undertaken) covering academic expenses, including tuition fees, uniforms, books, stationary, hostel mess fees, internet, transportation, and laptop .
• Mentorship support: Scholars receive guidance from Aimtron Foundation staff and volunteers to make better decisions in their academic journey.
• Networking opportunities: Scholars can network with other Aimtron Foundation scholars, alumni, and industry professionals.
• Career guidance: Scholars receive assistance to prepare for the job market and achieve their career goals.
• Students from Class 9 onwards can apply.
• Students should have secured minimum 65% marks in the previous qualifying examination.
• For single-parent children, the annual family income must be less than INR 3 lakh; for orphans, the guardian’s income or assets must be less than INR 3 lakh.
• Open only for Indian citizens.
• Children/wards of Aimtron Group employees are not eligible.
Overall, the Aimtron Foundation Scholarship program is a comprehensive support program for orphans or single-child parents to achieve their academic and career goals.
Selection Criteria:
• Academic merit
• Career Aspiration
• Financial need
• Community involvement
• Extracurricular activities
Note:
• Incomplete applications will not be considered.
• The decision of the selection committee is final and binding.
Community Service
Community events and volunteering among Aimtron employees is part of Employee Engagement.
As a part of our community involvement, various activities are organized in and around Tramba village in Rajkot.
Opened Library at Popular school, Tramba – Guiding youths to be an active generation of young people who are socially conscious!
- Health Awareness camps
- Blood Diagnosis camp
- Overall health checkup camps
- Blood Donation Drive
- Women Empowerment
- Tailoring classes
- Computer training classes
- Self defense training
- Vocational Training
- Spoken English workshop
- Communication & Presentation workshop
- Personality development workshop
- Apprenticeship in soldering
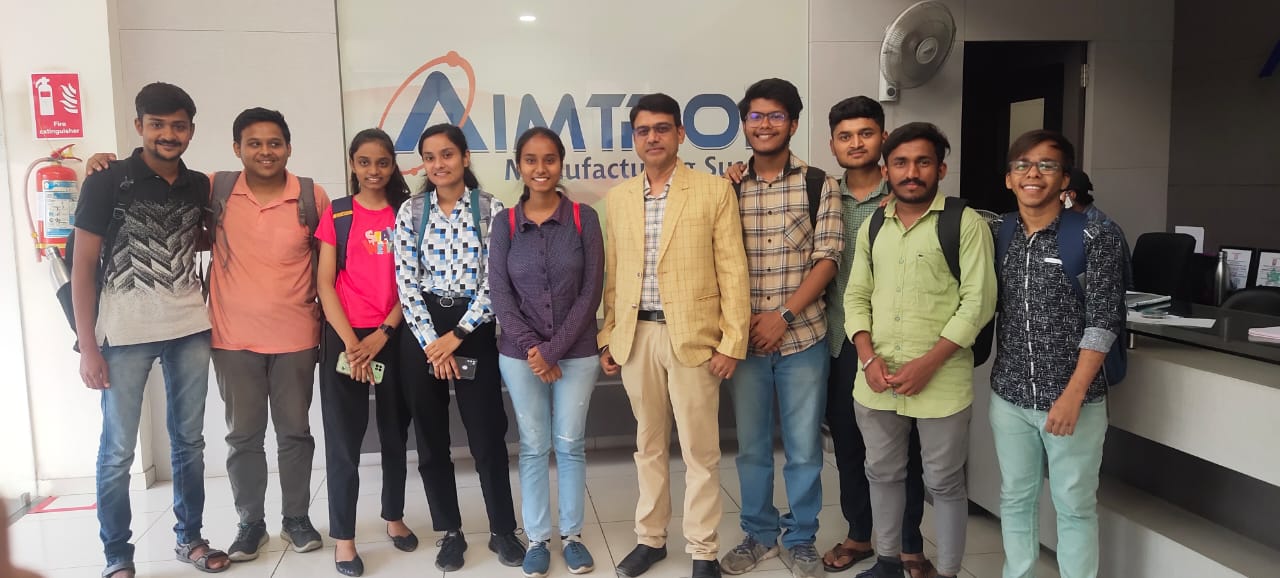
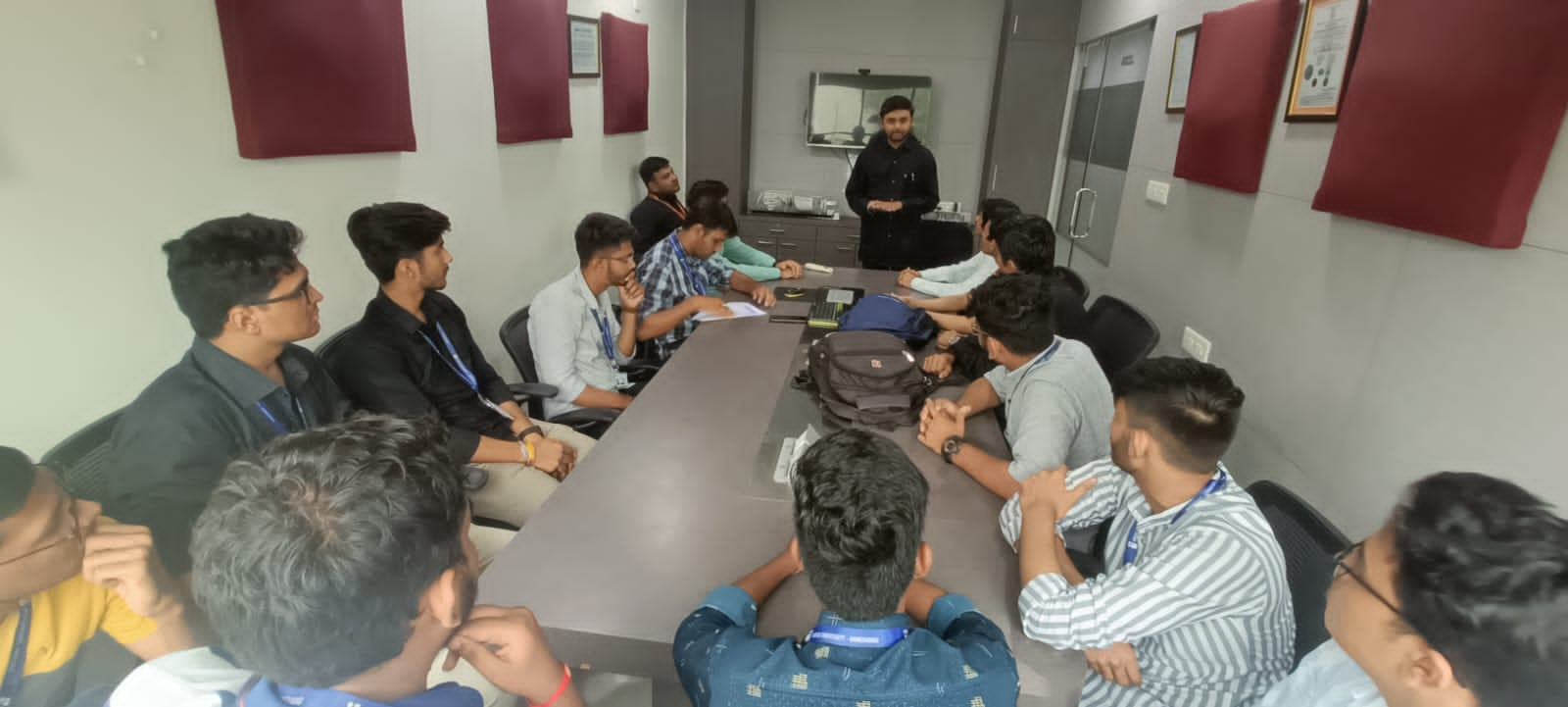
Internship Program / Industrial Visit
Internship Program
is designed for youths looking to expand to technical career pathways that help in bridging the gap between academia and the industry need.
Internship seeks to engage students pursuing Engineering Degrees or are Research Scholars enrolled in recognized University/Institution within Gujarat, Bangalore and USA as ‘interns’.
‘Interns’ shall be given exposure to various Verticals/Divisions/Units within “Aimtron” and would be expected to supplement the process of analysis within Aimtron through empirical collection and collation of in-house and other information.
Aimtron technologies opens up Internship Program, for engineering students or research scholars enrolled in recognized universities/institutions in Gujarat, Bangalore and USA.
P.S: Internship duration is as per college requirements, 2weeks, 4 weeks, 6 months and 1 year. Monday-Friday 10am to 5pm.
Registration Form – Apply Here
For technical issues relating to submissions online, please contact csr@aimtron.com.
Read more about Aimtron’s internship:
Download Guidelines Click Here
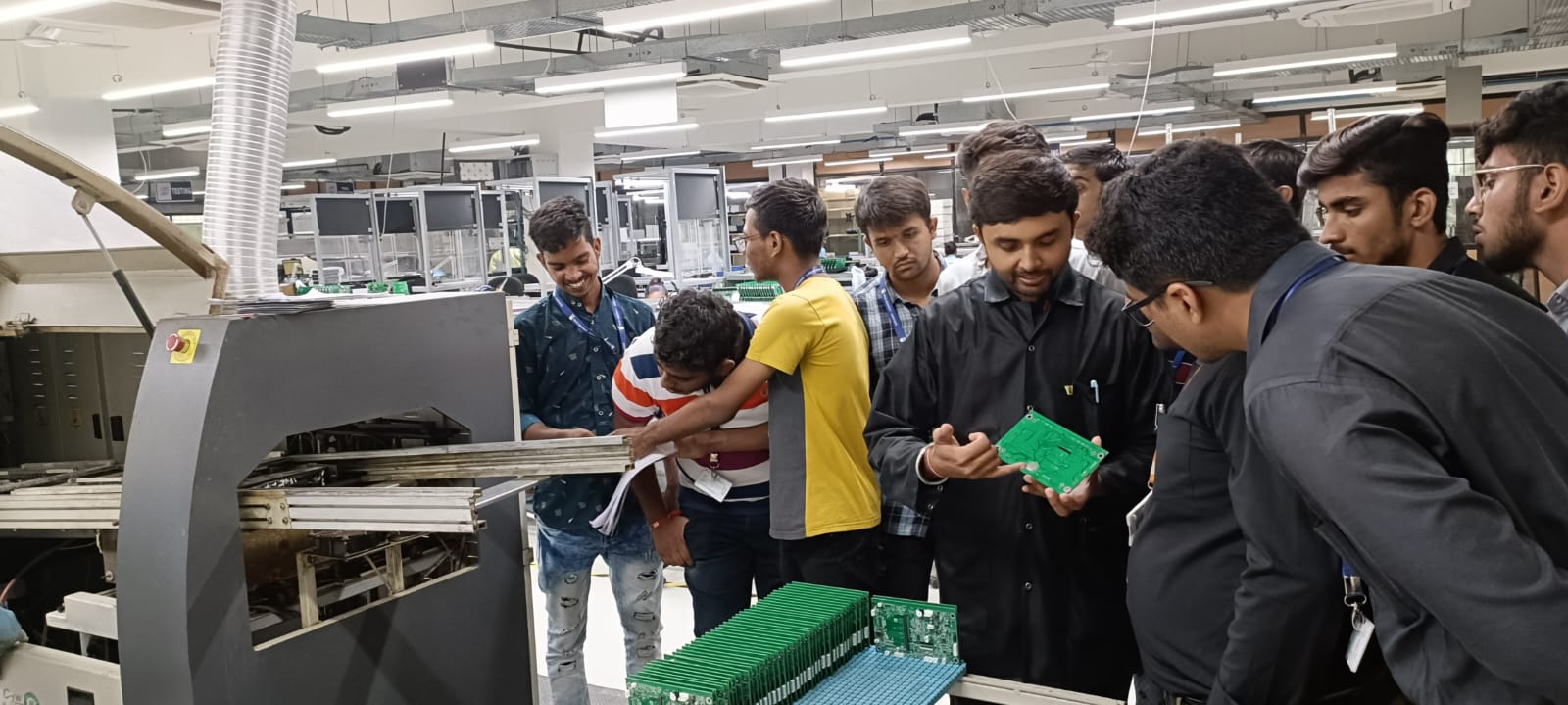
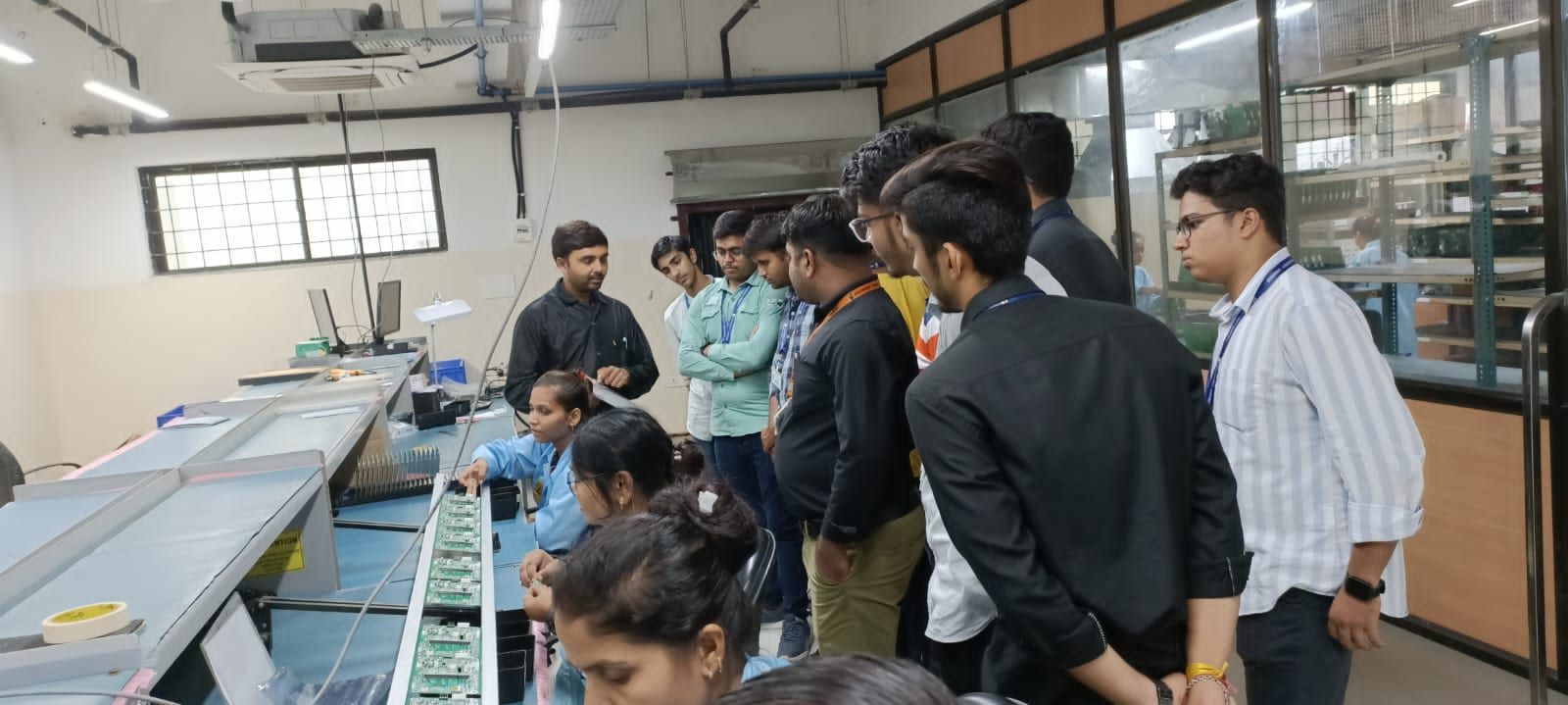
Industrial Visit
Experiential learning is a hands-on approach to education that emphasizes learning by doing. It is based on the idea that students learn best by experiencing things firsthand and reflecting on their experiences. Experiential learning can take many forms, such as internships, field trips, and service learning.
Industrial tour provides students a practical perspective of the work place, working methods and employment practices.
It gives exposure to current work practices as opposed to possibly theoretical knowledge being taught at institute.
Industrial tours provide an excellent opportunity to interact with industries and know more about industrial environment.
- Learn about our manufacturing process: Students will learn about the different steps involved in manufacturing the products, from raw materials to finished goods.
- See the production in action: Students will have the opportunity to see our production live and how it is being manufactured and tested.
- Meet with our employees: Students will have the opportunity to meet with our employees and learn about their jobs and experiences.
Registration Form – Apply Here
Courses / Knowledge Repository
We believe in the power of education to transform lives, which is why we’re thrilled to offer some free courses designed to inspire and empower students like you. Whether you’re looking to expand your knowledge, explore new interests, or enhance your skills, our curated collection of courses has something for everyone. Take the first step towards your educational journey by clicking the ‘Explore Courses’ button below and embark on a path of discovery with us.”
Knowledge Repository
Knowledge Repository: These are our collectibles from sessions taken by our Industry Experts across the world. These SME’s have taken out their valuable time and shared their knowledge. For the benefit of the students we have here a repository of some niche topics which can be accessed free to benefit from these exclusive deep dive sessions.
- Overview – Asic Chip Design and Development
- Flip Chip and Advanced Packaging Technologies
- Flux Chemistry & Standards
- Stencil Design
- Deep Dive Webinar – Profiling of reflow
- Solder Paste Basics & Handling
- IPs & Patents – Various Aspects!
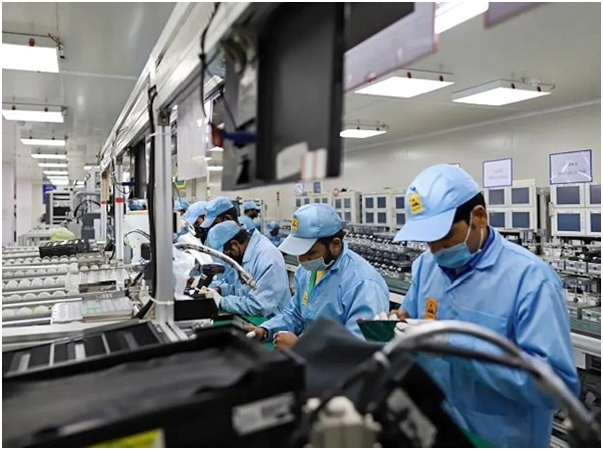

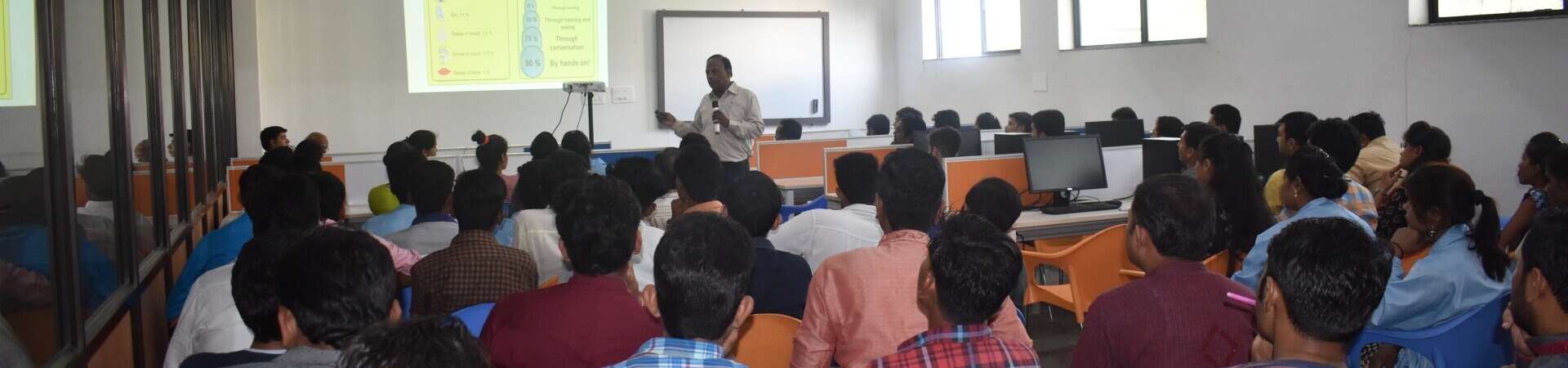
Webinar
Aim of these Webinars is to guide and help students to understand industry’s need and what industry is looking from engineering students. Webinars are conducted by Industry SMEs and Veterans. This will help you prepare to focus on the domains that you are interested in. You get to know the latest in the Industry and the growth in the industry.
If you are having difficulty filling out this form, please contact us.
For India:
Name: Sahana Hegde (Director-Skill development)
Email: csr@aimtron.com
Contact No: (+91) 7041735557
For USA:
Name: Nishtha Vasani (HR Management)
Email: nishtha@aimtron.com
Contact No: (+1) 224-688-0372
Technical Workshop
Assembly Line Operator
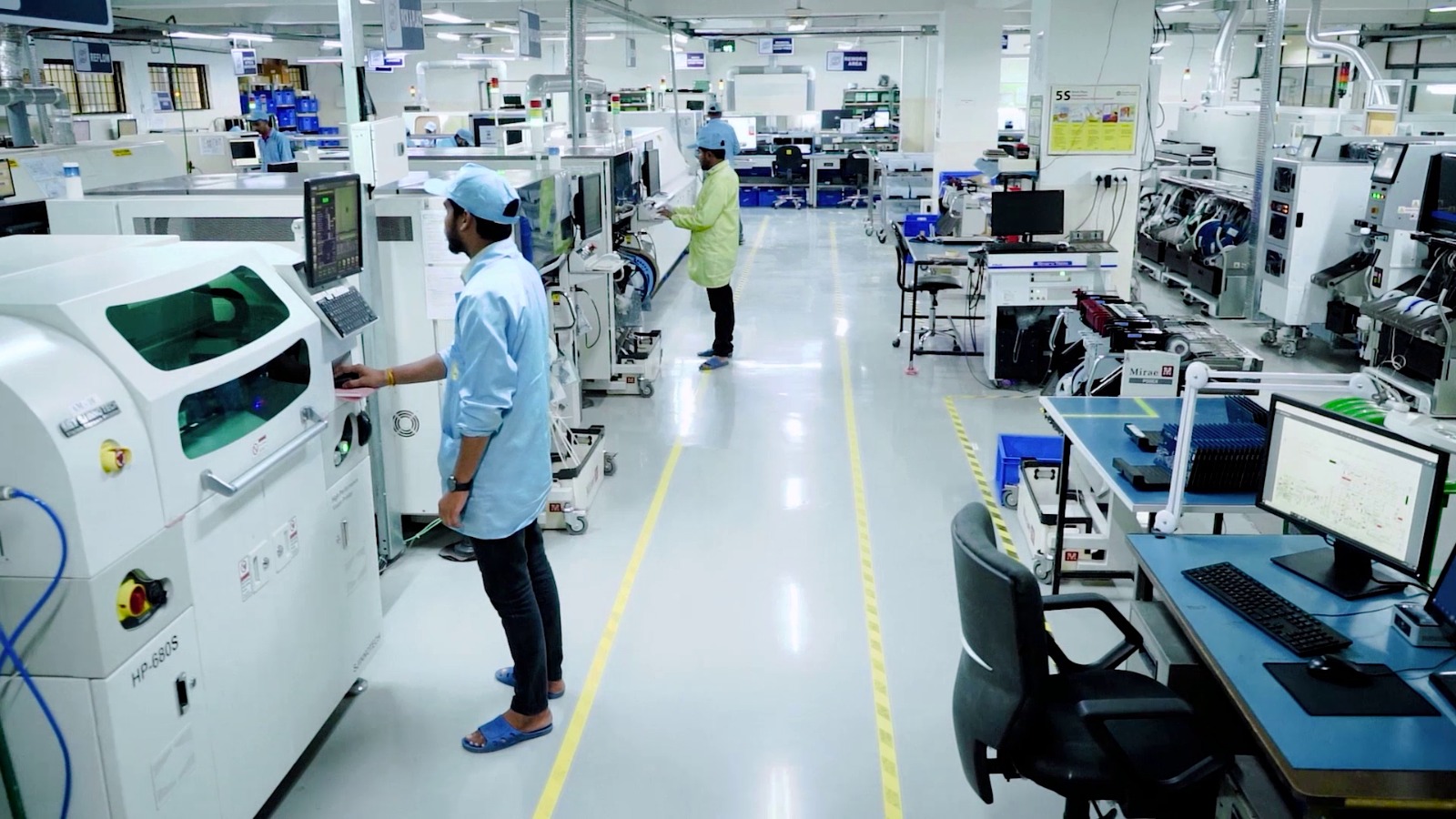

Brief Job Description
The individual at work is responsible for assembling the different modules in the IT hardware to complete the product. The individual receives different electronic and electromechanical modules, fits and assembles them together. The operator may assemble multiple modules and/or products by following operating procedures for different models.
Personal Attributes
The job requires the individual to work in a sitting or standing position for long hours on the assembly line.
The individual must be able to handle tools and equipment with precision and safely.
Applicable National Occupational Standards (NOS)
Description:
This OS unit is about receiving the components, modules, accessories and PCBs, and arranging for ease of assembling the product.
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Understanding work requirement
- Receiving the components and modules
- Assembling components
- Interacting with superior
Description:
This OS unit is about assembling the various modules and box assembly to complete the hardware product.
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Understanding work requirement
- Receiving modules to be assembled
- Assembling of modules
- Completing box assembly
- Interacting with superior
- Achieving productivity and quality standards
Description:
This unit is about effective, respectful communication and coordination with supervisors and colleagues.
Scope:
The scope covers the following:
- Communicate effectively with supervisor and colleagues
- Respect gender and ability differences
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Communicate effectively with supervisor and colleagues
- Respect gender and ability differences
Description:
This unit is about following health and safety procedures, waste management procedures and resource management in order to achieve required productivity and quality.
Scope:
The scope covers the following:
- Achieve optimum productivity and quality
- Implement health and safety procedures
- Organise waste management and recycling
- Conserve resources
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Achieve optimum productivity and quality
- Implement health and safety procedures
- Organise waste management and recycling
- Conserve resources
Description:
This unit is about employability skills, Constitutional values, becoming a professional in the 21st Century, digital, financial, and legal literacy, diversity and Inclusion, English and communication skills, customer service, entrepreneurship, and apprenticeship, getting ready for jobs and career development.
Scope:
The scope covers the following:
- Introduction to Employability Skills
- Constitutional values – Citizenship
- Becoming a Professional in the 21st Century
- Basic English Skills
- Communication Skills
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Financial and Legal Literacy
- Essential Digital Skills
- Entrepreneurship
- Customer Service
- Getting ready for Apprenticeship & Jobs
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Introduction to Employability Skills
- Constitutional values – Citizenship
- Becoming a Professional in the 21st Century
- Basic English Skills
- Communication Skills
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Financial and Legal Literacy
- Essential Digital Skills
- Entrepreneurship
- Customer Service
- Getting ready for apprenticeship & Jobs
In Process & Quality Engineer
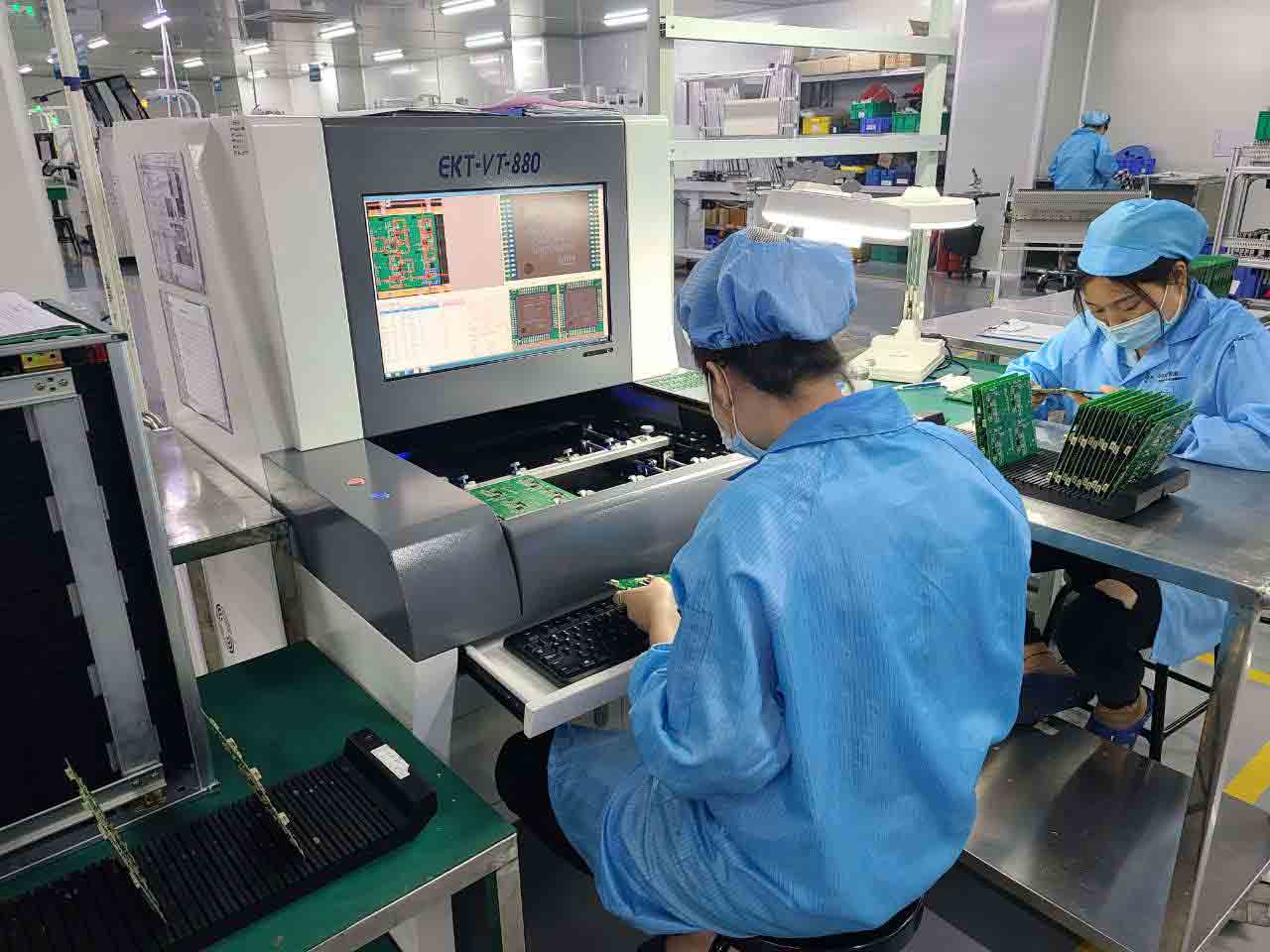

Brief Job Description
The individual at work sample checks final PCB assembly for functional conformance as well as visually before they are packed and dispatched. The individual is responsible for ensuring total quality or IPC or ISO standards compliance during the assembly of PCBs.
Personal Attributes
The job requires the individual to have attention to detail, ability for implementing process standardisation, good eyesight, and command over test tools and equipment.
Applicable National Occupational Standards (NOS)
Description:
This OS unit is about checking PCB after every stage of assembly up to the final stage and ensure than quality is maintained for the final assembled processes as well as in the process of assembly
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Understanding work requirement
- Performing Quality Check
- Completing the QC process
- Achieving productivity and quality standards
Description:
This unit is about the communicating and managing work effectively at the workplace as well as taking measures to enhance own competence and working in a disciplined and ethical manner.
Scope:
The scope covers the following:
- Communicate effectively at the workplace
- Work effectively
- Maintain and enhance professional competence
- Work in a disciplined and ethical manner
- Uphold social diversity at the workplace
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Communicate effectively at the workplace
- Work effectively
- Maintain and enhance professional competence
- Work in a disciplined and ethical manner
- Uphold social diversity at the workplace
Description:
This OS unit is about knowledge and practices relating to health, safety and security that candidates need to use in the workplace.
Scope:
The scope covers the following:
- Deal with workplace hazards
- Apply fire safety practices
- Follow emergencies, rescue and first-aid procedures
- Effective waste management/recycling practices
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Deal with workplace hazards
- Apply fire safety practices
- Follow emergencies, rescue and first-aid procedures
- Effective waste management/recycling practices
PCB Assembly Operator
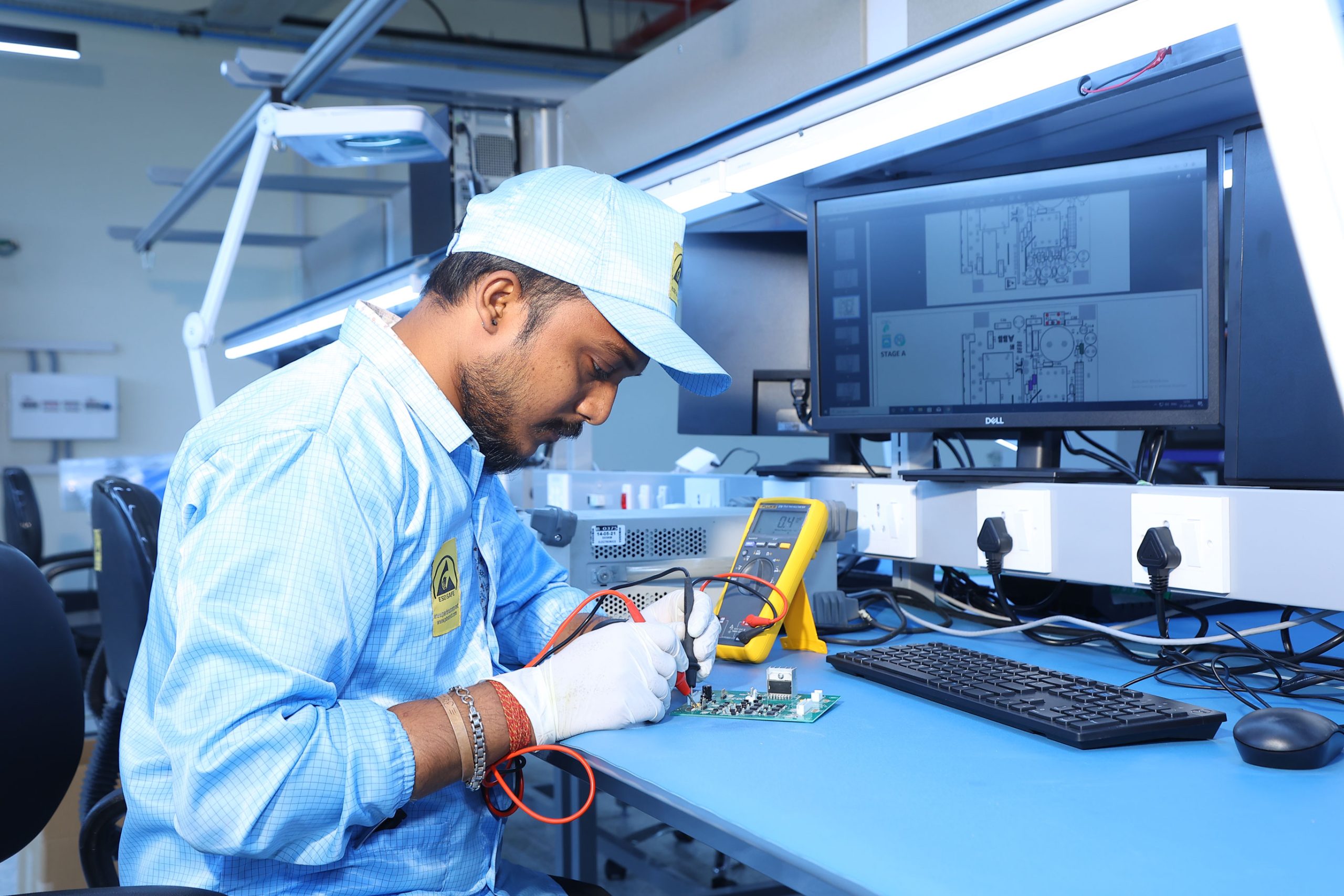

Brief Job Description
The individual on the job is responsible for manually placing different types of components on the PCB as per the design requirements and then soldering them.
Personal Attributes
The job requires the individual to have attention to details, good eyesight, and ability to work for long hours generally in a sitting position.
Applicable National Occupational Standards (NOS)
Description:
This OS unit is about inserting the components on the printed circuit boards (PCB) manually and then soldering them
Scope:
This unit/task covers the following:
- Insert components on the board manually
- Perform visual check
- Achieve productivity and quality standards
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Inserting components manually
- Performing visual check
- Achieving productivity and quality standards
Description:
This OS unit is about communicating, coordinating and maintaining proper relationship with colleagues and seniors in order to achieve smooth workflow.
Scope:
This unit/ task covers the following:
- Interact with supervisor or superior
- Coordinate with colleagues
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Interacting with supervisor
- Interacting with colleagues
Description:
This OS unit is about following safety procedures, communicating potential hazards and dangers of accidents on the job
Scope:
This unit/ task covers the following:
- Understand potential sources of accidents
- Use safety gear to avoid accidents
- Understand the safety procedures followed by the company
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Understanding potential sources of accidents
- Using safety gear
- Understanding of safety procedures
- Following daily safety measures
- Communicating to supervisor
Pick and Place Assembly Operator
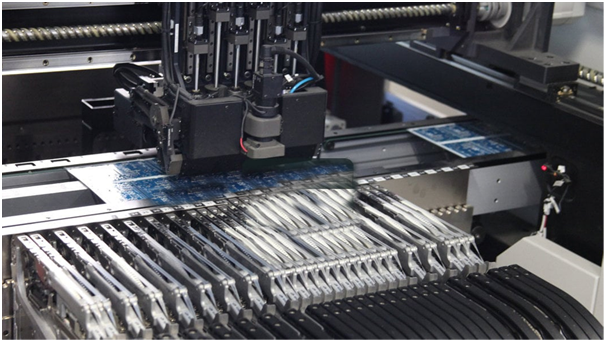
Brief Job Description
A Pick-and-Place Assembly Operator at work programs, operates and maintains the automated pick-and-place machine for placing different types of components on the surface of PCBs for soldering.
Personal Attributes
The job requires the individual to have: attention to details, good eyesight and visual accuracy and to work for long hours generally in a standing position.
Applicable National Occupational Standards (NOS)
Description:
This OS unit is about assembling surface-mount components on the printed circuit boards (PCB) by operating the automated pick-and-place machine after loading with reels of components and program as well as maintaining the machine.
Scope:
The scope covers the following:
- Program and load the pick and place machine
- Load components and operate the machine for assembling on PCBs
- Inspect assembly cycle for completion
- Perform preventive maintenance of the machine
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Program and load the pick and place machine
- Load components and operate the machine for assembling on PCBs
- Inspect assembly cycle for completion
- Perform preventive maintenance of the machine
Description:
This unit is about the communicating and managing work effectively at the workplace as well as taking measures to enhance own competence and working in a disciplined and ethical manner.
Scope:
The scope covers the following:
- Communicate effectively at the workplace
- Work effectively
- Maintain and enhance professional competence
- Work in a disciplined and ethical manner
- Uphold social diversity at the workplace
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Communicate effectively at the workplace
- Work effectively
- Maintain and enhance professional competence
- Work in a disciplined and ethical manner
- Uphold social diversity at the workplace
Description:
This OS unit is about knowledge and practices relating to health, safety and security that candidates need to use in the workplace.
Scope:
The scope covers the following:
- Deal with workplace hazards
- Apply fire safety practices
- Follow emergencies, rescue and first-aid procedures
- Effective waste management/recycling practices
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Deal with workplace hazards
- Apply fire safety practices
- Follow emergencies, rescue and first-aid procedures
- Effective waste management/recycling practices
Description:
This unit is about employability skills, Constitutional values, becoming a professional in the 21st Century, digital, financial, and legal literacy, diversity and Inclusion, English and communication skills, customer service, entrepreneurship, and apprenticeship, getting ready for jobs and career development.
Scope:
The scope covers the following:
- Introduction to Employability Skills
- Constitutional values – Citizenship
- Becoming a Professional in the 21st Century
- Basic English Skills
- Career Development & Goal Setting
- Communication Skills
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Financial and Legal Literacy
- Essential Digital Skills
- Entrepreneurship
- Customer Service
- Getting ready for Apprenticeship & Jobs
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Introduction to Employability Skills
- Constitutional values – Citizenship
- Becoming a Professional in the 21st Century
- Basic English Skills
- Career Development & Goal Setting
- Communication Skills
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Financial and Legal Literacy
- Essential Digital Skills
- Entrepreneurship
- Customer Service
- Getting ready for apprenticeship & Jobs
Thru-Hole Assembly Operator
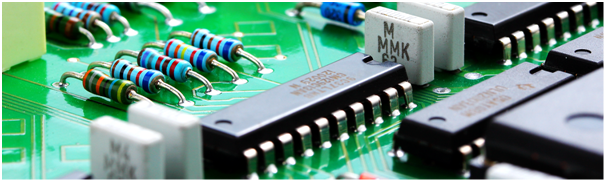
Brief Job Description
A Through-hole Assembly Operator is responsible for manually fixing components using hand tools, operating and maintaining the automated insertion machine used for placing different types of components on the through-hole PCBs.
Personal Attributes
The job requires the individual to have attention to details, good eyesight, and ability to work for long hours generally in a standing or sitting position.
Applicable National Occupational Standards (NOS)
Description:
This OS unit is about assembling through-hole components on the printed circuit boards (PCB) manually or by operating the automated insertion machine.
Scope:
The scope covers the following:
- Mount the components on the PCB
- Operate the through-hole machine for automated assembling
- Undertake preventive maintenance of the machine
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Mount the components on the PCB
- Operate the through-hole machine for automated assembling
- Undertake preventive maintenance of the machine
Description:
This unit is about the communicating and managing work effectively at the workplace as well as taking measures to enhance own competence and working in a disciplined and ethical manner.
Scope:
The scope covers the following :
- Communicate effectively at the workplace
- Work effectively
- Maintain and enhance professional competence
- Work in a disciplined and ethical manner
- Uphold social diversity at the workplace
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Communicate effectively at the workplace
- Work effectively
- Maintain and enhance professional competence
- Work in a disciplined and ethical manner
- Uphold social diversity at the workplace
Description:
This OS unit is about knowledge and practices relating to health, safety and security that candidates need to use in the workplace.
Scope:
The scope covers the following:
- Deal with workplace hazards
- Apply fire safety practices
- Follow emergencies, rescue and first-aid procedures
- Effective waste management/recycling practices
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Deal with workplace hazards
- Apply fire safety practices
- Follow emergencies, rescue and first-aid procedures
- Effective waste management/recycling practices
Description:
This unit is about employability skills, Constitutional values, becoming a professional in the 21st Century, digital, financial, and legal literacy, diversity and Inclusion, English and communication skills, customer service, entrepreneurship, and apprenticeship, getting ready for jobs and career development.
Scope:
The scope covers the following:
- Introduction to Employability Skills
- Constitutional values – Citizenship
- Becoming a Professional in the 21st Century
- Basic English Skills
- Career Development & Goal Setting
- Communication Skills
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Financial and Legal Literacy
- Essential Digital Skills
- Entrepreneurship
- Customer Service
- Getting ready for Apprenticeship & Jobs
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Introduction to Employability Skills
- Constitutional values – Citizenship
- Becoming a Professional in the 21st Century
- Basic English Skills
- Career Development & Goal Setting
- Communication Skills
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Financial and Legal Literacy
- Essential Digital Skills
- Entrepreneurship
- Customer Service
- Getting ready for apprenticeship & Jobs
FOD Control for Electronics Manufacturing

Course Description
This course introduces participants to the causes of FOD and the steps you can take to mitigate its effects when handling, storing, or transporting items in a manufacturing facility.
Course Objective
To understand the concept of FOD which will be able to employ the key tools, materials, and processes designed to prevent and control the effects of FOD within a manufacturing facility.
Description:
- Define FO Debris and FO Damage
- Differentiate between foreign object debris and FO damage
- Distinguish foreign object debris by category
- Identify FOD material composition & sources
- Identify resources available for FOD prevention and control
Description:
- Distinguish FOD areas and classify them by the degree of control and potential impact
- Differentiate area signage
- Become familiar with facility and environmental controls
Description:
- Identify work environment controls and practices employed to prevent FOD
- Identify and describe restricted personal items in FOD sensitive areas
- Distinguish and describe controls for tools, hardware and consumables used in a designated FOD area
Description:
- Identify documentation that contains guidance for FOD prevention
- Identify the industry best practices for FOD prevention
- Identify the various elements of a FOD control plan
- Identify responsibilities of the FOD focal point
- Identify whether training, escorted access, or unescorted access are options for
- personnel entering a FOD control area
- Identify steps for containment and removal of FOD
- Select from a list, examples that will require a FOD incident report
Safety practices for Electronics Manufacturing

Course Description
This course introduces participants to the most common safety practices and workplace hazards in electronics manufacturing.
Course Objective
To understand the safety practices and workplace hazards which will be able to employ the key tools, materials, and processesdesigned to keep you and your coworkers safe within a manufacturing facility.
Description:
- Define the risks associated with electronic assembly processes
- Describe the best practices of workplace safety
- Identify the basic types of safety signage for workers
- Identify hazards that can be minimized by the use of PPE
- Identify safety concerns related to improper handling
Description:
- Identify the risks and precautions related to electrical safety
- Identify the risks and precautions related to chemical safety
- Identify the potential risks associated with the soldering process
- Identify the potential risks associated with the use of radiation-based equipment
Description:
- Describe various risks associated with tools and equipment used in the electronic
- assembly
ESD Control for EMS

Course Description
This course introduces participants to the causes of ESD and the steps you can take to mitigate its effects when handling, storing, or transporting ESD sensitive components in a manufacturing facility. These preventive measures and their application are based on ANSI/ESD S20.20 and other relevant standards.
Course Objective
To understand the concept of ESD which will be able to employ the key tools, materials, and processesdesigned to prevent and control the effects of ESD within a manufacturing facility.
Description:
- Define Electrostatic discharge
- Explain what causes an electrostatic discharge
- Define triboelectric charging (triboelectric effect)
- Explain the difference between conductive and insulative materials
- Explain catastrophic vs. latent failure
- Describe typical static charge sources
- Explain the benefits of controlling ESD
Description:
- Explain the use of grounding for controlling ESD in the workplace
- Identify common types of personnel grounding devices
- Describe the proper use of ESD wrist straps, ESD shoes, shoe grounders, and constantmonitoring devices
- Explain the testing procedure for personnel grounding devices
- Describe safe handling and transportation procedures for ESDS items
Description:
- Explain how facilities mitigate the effect of ESD with ESD Protected Areas (EPAs)
- Identify the tools and best practices for maintaining an ESD safe workstation
- Explain the purpose, function, and strategies for using ESD safe packaging
Wire Harness Assembly for Operators

Course Description
This program was developed to meet a significant challenge faced by wire harness manufacturers: Quickly onboarding wire harness assemblers to produce quality products in the ever-shrinking time frames demanded by customers. To provide the specific set of knowledge and skills that every operator needs to build quality wires and cable harnesses all contained in this training.
This course introduces the key tools, materials, and processes for operators working in wire harness assembly. Operators can complete the core set of modules to receive knowledge on wire harness assembly.
Wire Harness Assembly for Operators is accredited by the ANSI National Accreditation Board under ANSI/ASTM E2659-18, Standard Practice for Certificate Programs.
Course Objective
To understand the key tools, materials, and processes required to wire harness assembly and the student will be able to perform basic wire harness assembly processes within a manufacturing facility.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES PER COURSE MODULE
Description:
- Describe wire harness assemblies and what led to their introduction
- Distinguish benefits of wire harness assemblies compared to individual wires
- Identify common uses of wire harness assemblies
- Explore reasons why wire harness assemblies require high quality workmanship
Description:
- Identify standard safety signage and symbols for assembly operators
- Describe standard safety procedures for protecting assembly operators and equipment
- Identify potential risks and hazards of standard materials used by wire harness
- assembly operators
- Describe safety concerns of using common wire harness assembly tools and equipment
Description:
- Identify types of engineering documentation used in wire harness assembly
- Explain how engineering drawings are used as a build reference
- Describe the relationship of work instructions, assembly sequence, and reference
- specifications
- Identify components of a Bill of Materials
Description:
- Identify properties of solder, flux, adhesive, and potting/encapsulation
- Identify types of wires and cables used in wire harness assembly
- Distinguish wire insulation types and gauge
- Recognize terminal types
- Identify common connector types
Description:
- Explore common tools and equipment used in wire harness assembly
- Identify measurement tools used in wire harness assembly
- Distinguish methods for taking accurate physical measurements
- Define tool calibration process
Description:
- Explain steps in wire preparation and processing
- Define requirements for measuring cables and wires
- Describe methods for measuring, cutting, stripping, and tinning wire
- Identify inspection criteria for wire preparation
Description:
- Identify common IPC standards used by wire harness assembly operators
- Explain the need for inspection and describe the use of magnification
- Identify common electrical and mechanical tests used in wire harness assembly
Description:
- Explain differences between crimping methods
- Identify acceptable and defect conditions for open barrel crimp terminations
- Identify acceptable and defect conditions for closed barrel crimp terminations
- Identify acceptable and defect conditions for machined crimp terminations
Description:
- Identify types of soldered terminations
- Explain processes for attaching wires to terminals
- Differentiate between acceptable and defect conditions for soldered terminations
Description:
- Identify the purpose of wire splices
- Explain the process of soldered, crimped, and ultrasonic wire splices
- Apply acceptance criteria for soldered, crimped, and ultrasonic wire splices
Description:
- Describe characteristics of connectors used in wire harness technology
- Explain the purpose of strain relief and braid terminations in connectors
- Differentiate crimping and soldering methods of connectorization
- Apply methods for inspecting and testing connector assemblies
Description:
- Describe parts of a coaxial cable
- Identify types of coaxial cables
- Distinguish most common coaxial cable connector types
- Describe common coaxial cable preparation steps
- Identify coaxial cable and connector assembly methods
Description:
- Describe requirements for labelling wire harness assemblies
- Identify label types and acceptance criteria
- Evaluate label placement and location
- Identify common securing devices
- Describe effects of improper tension of securing devices
- Identify common wire harness coverings
Description:
- Recognize requirements for hardware installation
- Distinguish criteria for wire harness installation
- Identify conditions for finished assembly installation
Wire Harness Assembly Acceptance Criteria for Operators
Course Description
This course provides a practical introduction to the terms, concepts, and acceptably criteria of the Wire Harness Assembly as they apply to the role of the operators, technicians, and other assembly line staff.
Course Objective
To understand the acceptance criteria of wire harness assembly and effectively navigate, locate, and apply the criteria specified in the applicable standard in your role as an electronics assembly line operator, technician, or supervisor within a manufacturing facility.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES PER COURSE MODULE
Description:
- Identify scope and purpose of IPC/WHMA-A-620 standard
- Navigate IPC/WHMA-A-620 using table of contents
- Recognize product classifications
- Recognize acceptable, process indicator, and defect conditions
- Demonstrate ability to read and apply criteria in IPC/WHMA-A-620
- Differentiate between System International (SI) and Imperial English Units of measurement
- Recognize order of precedence
- Identify requirements for handling, safety, and ESD protection
- Identify requirements for tools and equipment
- Differentiate between rework and repair
Description:
- Define general requirements for wire preparation
- Identify conductor and insulation defects
- Define requirements for measuring cables and wires
- Describe in-process and final acceptance requirements for electrical and mechanical testing
Elements and Performance Criteria:
- Describe requirements for soldered terminations
- Identify materials, tools, and equipment used in hand-soldered terminations
- Distinguish types of solder alloy
- Describe criteria for soldered connections subject to high voltages
Description:
- Describe requirements for crimp terminations
- Identify materials, tools, and equipment used in crimp terminations
- Distinguish between open and closed barrel terminations
- Describe requirements for insulation displacement connections and discrete wire terminations
- Identify requirements for splices produced through hand soldering and crimping
Description:
- Identify requirements for insulation clearance and weld nugget
- Describe requirements for hardware mounting, strain relief, sleeving, and boots
- Identify common defect conditions related to connectorization
- Distinguish methods of encapsulating components, such as molding and potting
- Identify requirements for molded and potted components
Description:
- Identify requirements for marking and labelling cable and wire harness assemblies
- Identify requirements for securing cable and wire harness assemblies
- Distinguish methods for securing cable and wire harness assemblies
Description:
- Identify requirements for braided shielding and shield termination
- Describe materials used in electrical shielding
- Distinguish types of protective coverings, including braiding, heat shrink tubing, and taping
- Identify requirements for protective coverings
Description:
- Identify requirements and acceptance criteria for coaxial, biaxial, and multiaxial cable assemblies
- Describe general requirements for finished assembly installation
- Identify requirements for hardware installation, torque, and stress relief
Electronics Assembly for Operators
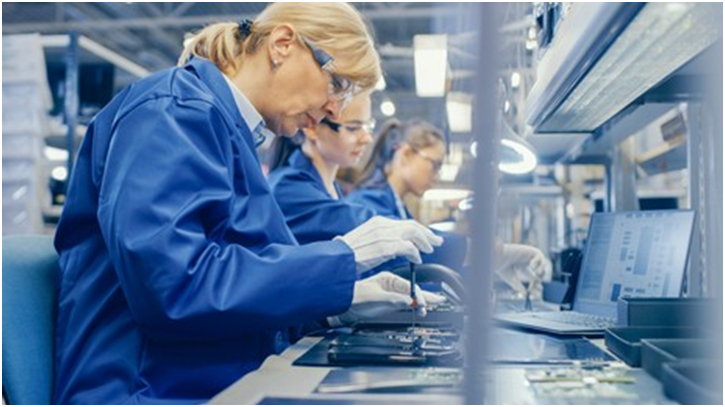

Course Description
This course introduces the key concepts, tools, materials, and processes for operators working in electronics assembly. Participants can complete the core set of modules to receive their certificate of qualification, then select among nine voluntary modules for process-specific training. After completing this course, participants will be able to employ the correct procedures for building Printed Circuit Board Assemblies (PCAs) within an electronics manufacturing facility.
Electronics Assembly for Operators is accredited by the ANSI National Accreditation Board under ANSI/ASTM E2659-18, Standard Practice for Certificate Programs.
Course Objective
To understand the key tools, materials, and processes required to assemble Printed Circuit Board Assemblies (PCAs) within an electronics manufacturing facility.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES PER COURSE MODULE
Description:
- Explain the difference between a printed circuit board (PCB) and a printed circuit board assembly (PCA)
- Identify the common features of a printed circuit board
- Identify the common features of a printed circuit board assembly
- Describe the most common methods used to attach components to printed circuit board assemblies.
Description:
- Describe and distinguish the surface mount (SMT) and through-hole (TH) assembly processes
- Identify the different post-processes used in electronics assembly
Description:
- Describe the role that IPC standards play in the electronics manufacturing industry
- Identify the standards most widely used in the assembly process
- Distinguish between Class 1, 2, and 3 electronics products
- Compare IPC certification with IPC training programs
Description:
- Identify standard safety signs and symbols relevant to assembly operators
- Describe standard safety procedures for protecting assembly operators, equipment, and products
- Identify potential risks and hazards of standard materials used by assembly operators
- Describe safety concerns of using standard assembly equipment
Description:
- Identify the cause and concerns of electrostatic discharge (ESD) in electronics assembly
- Describe the function of personal grounding and static control devices
- Demonstrate proper handling procedures for PCBs and PCAs
- Describe the cause and prevention of foreign object debris (FOD)
Description:
- Differentiate between through-hole and surface mount components
- Distinguish between active and passive components
- Identify the most common types of components used in electronics assembly
- Place components on a PCB based on polarity and orientation
- Differentiate between wires, cables, and harnesses
- Identify types of terminals used in electronics assembly
Description:
- Identify the sections of a bill of materials, engineering drawing, and work instructions
- Explain how operators use a bill of materials, engineering drawing, and work instructions during the electronics assembly process
- List the order of precedence for assembly documentation
Description:
- Define quality in electronics manufacturing
- Identify quality conditions according to IPC standards
- Explain the best practices used to inspect electronic assemblies
- Explain the purpose of the most common measuring tools used to inspect electronic assemblies
- Identify common defects found on printed circuit board assemblies
Description:
- Describe the hand soldering process and its properties
- Explain the function of common hand soldering tools, equipment, and materials
- Identify common hand soldering defects and soldering anomalies
Description:
- Identify machines used in surface mount technology (SMT) assembly process
- Describe steps in surface mount technology (SMT) assembly process
- Define the reflow soldering process for SMT assemblies
- Identify the cause and types of SMT defects within the soldering process
Description:
- Identify the purpose of through-hole technology in electronics assembly
- Identify common tools, materials, and equipment used
- Describe the steps for both the manual and automatic through-hole assembly processes
- Identify the common through-hole assembly defects
Description:
- Recognize common types of wires and cables
- Use wire and cable preparation tools
- Prepare wires and cables
- Detect common wire preparation defects
Description:
- Identify different types of terminals used in electronics assembly
- Identify the methods used to attach terminals to wires
- Differentiate between soldered and crimped terminations
- Recognize acceptable soldered and crimped termination conditions
- Identify common soldered and crimped termination defects
Description:
- Identify types of connectors used in wire harness technology
- Distinguish methods of connectorization
- Distinguish methods for making and evaluating wire splices
- Describe the wire harness assembly process
Description:
- Identify common tools, hardware, and materials associated with electronics assembly
- Explain how specific assembly tools and hardware are used during the installation process
Description:
- Identify equipment, tools, and materials used to apply conformal coating
- Explain steps in conformal coating process
- Classify causes and characteristics of conformal coating defects
Scope:
Press Fit
Description:
- Identify tools, equipment, and materials used in press-fit insertion
- Describe the individual steps of the press-fit insertion process
- Identify common press-fit insertion defects
Description:
Participants must complete the Final Exam for Modules 1 through 8 with a passing score of 80% to access and download their Qualified Assembly Operator Certificate. Students may attempt the exam up to three (3) times. Please note that a third and final attempt is permitted after 24 hours of the second attempt.
Inspection of Electronic Assemblies: Introduction

Course Description
Trains participants to perform “Quality Inspection” using the essential tools, materials, and processes that deliver consistent quality products. Introduction course introduces participants to the essential tools, materials, and processes that all inspectors must use to perform their role to industry-levels of proficiency.
Course Objective
After successfully completing this course, participants/ operators will be able to apply their understanding of acceptability standards, inspection methods and tools, documentation, and component characteristics to perform incoming and product level inspection.
Description:
- Identify the most common IPC standards used by electronics assembly inspectors
- Use the product class and condition criteria in IPC standards to determine the acceptability of the parts and components on a PCB assembly
- Use the table of contents, index, and appendices to quickly navigate IPC standards
- Explain how metric and imperial units of measurement are used in IPC standards
- Explain how more than, less than, and equal to symbols are used in IPC standards
- Use figures, illustrations, and tables to determine the acceptability of the parts and components on a PCB assembly
- Demonstrate effective strategies for interpreting acceptability criteria, including figures and illustrations, tables, and units of measurement
- Explain common industry-specific terms employed by inspectors
Description:
- Explain Standard Inspection Protocol (SIP) and order of precedence
- Differentiate between visual, X-ray, and Automated Optical inspection methods
- Use work instructions and IPC standards to select the correct magnification power for visual inspection
- Perform visual inspection with common magnification tools such as loupes and microscopes
- Use rulers, calipers, micrometers, go-no-go gauges and pull testers to perform visual inspection
- Verify the calibration labels of measurement tools
- Demonstrate recommended techniques to visually identify and document potential defects
Description:
- Identify the different parts of an assembly drawing
- Use an assembly drawing to verify that the visible features of an assembly meet customer specifications
- Explain the role of GD&T symbols in assembly drawings
- Explain the function and contents of work instructions and Bill of Materials (BOM)
- Use work instructions to inspect an assembly according to customer specifications
- Use a Bill of Materials to confirm the presence of specific parts materials listed in an assembly drawing
- Explain the purpose of referenced specifications
Description:
- Identify and distinguish the characteristics of through-hole and surface-mount components
- Recall the processes used to mount through-hole and surface-mount components
- Identify and distinguish component packages and component packaging
- Identify the most common types of components used in electronics assembly
- Describe the purpose of common electronic components
- Use documentation, component reference designators, sample boards, and markings on components and PCAs to verify that the right components have been correctly placed and oriented on an assembly
Description:
- Explain the importance of a well-developed incoming inspection plan
- Identify the various steps of a typical incoming inspection process
- Inspect materials, parts, and packaging for signs of damage
- Use documentation to verify that incoming parts and materials conform to customer specifications
- Use documentation to determine proper storage for materials
- Use documentation to verify that PCB dimensions, markings, and solder mask conform to quality requirements and customer specifications
- Identify common measurement and testing methods used for incoming materials and printed boards
Standard acceptability criteria for Electronics assembly for operators
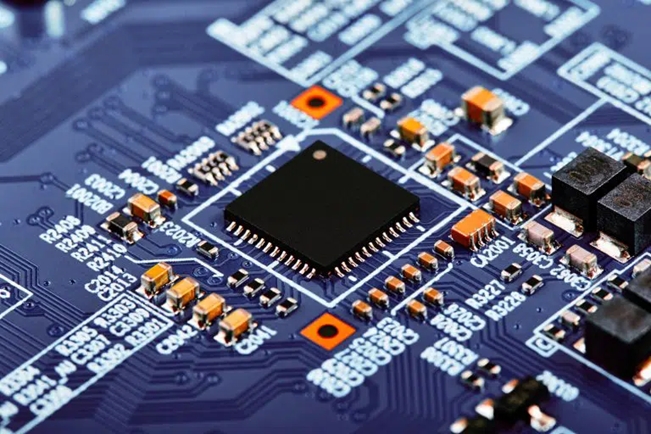
Course Description
To provide a practical introduction to the terms, concepts, and acceptability requirements of the electronics assembly standard as they apply to the role of the electronics assembly line operator, technician, or supervisor and inspector.
Course Objective
To understand the acceptability criteria of a printed circuit board assembly as specified in the standard. Also, effectively navigate, locate, and apply the criteria specified for electronics assembly.
Description:
- Identify scope and purpose of IPC-A-610 standard
- Navigate IPC-A-610 using table of contents and index
- Recognize product classification
- Recognize target, acceptable, process indicator, and defect conditions
- Differentiate between System International (SI) and Imperial English Unit of measurement Identify order of precedence
- Understand how to use magnification tables
- Explain how to handle electronic assemblies to minimize or prevent electrostatic discharge
Description:
- Identify acceptability requirements for hardware
- Describe requirements for electrical clearance and torque
- Identify acceptability requirements for soldered connections
- Distinguish common soldering anomalies
- Identify criteria for high voltage connections
- Identify acceptability requirements for terminal connections
- Describe process for attaching leads and wires to terminals
- Distinguish types of conductor and insulation damage
- Identify acceptability requirements for surface mount (SMT) assemblies
- Distinguish dimensional criteria for rectangular or square chip components
- Describe criteria for assessing damage to electronic components
- Identify acceptability requirements for through hole (TH) technology
- Distinguish between supported and unsupported through holes
- Describe inspection methodology for SMT and TH components
- Identify acceptability requirements for printed circuit boards (PCB) and assemblies (PCA)
- Distinguish types of laminate, conductor, and lands defects
- Identify requirements for cleanliness for PCAs/PCBs
- Identify acceptability requirements for discrete wiring and solderless wrap connections
Standard Requirements for Soldered Electrical and Electronics Assemblies

Course Description
To provide a practical introduction to the terms, concepts, and acceptability requirements of the electronics assembly standard as they apply to the role of the electronics assembly line operator, technician, or supervisor.
Course Objective
To understand the basic tools, materials, and processes required to build a printed circuit board assembly within an electronics manufacturing facility. Also, effectively navigate, locate, and apply the criteria specified for electronics assembly.
Description:
- Identify scope and purpose of J-STD-001 standard
- Navigate J-STD-001 using table of contents
- Recognize product classifications
- Distinguish acceptable, process indicator, and defect conditions
- Demonstrate ability to read and apply criteria in J-STD-001
- Differentiate between System International (SI) and Imperial English Units of measurement
- Identify order of precedence
- Understand common terms used in J-STD-001
Description:
- Identify requirements for materials, including solder alloys and flux
- Identify components, tools, and equipment requirements
- Define solderability and requirements for component surface finishes removal
- Recognize thermal protection and handling parts requirements
- Identify soldering connection requirements and acceptance
- Describe product assurance requirements
- Describe rework and repair process requirements
Description:
- Identify basic requirements and acceptance for wire preparation and terminal mounting
- Describe requirements for soldering to terminals
- Distinguish requirements for jumper wires
- Differentiate between supported and unsupported holes
- Identify lead protrusion requirements
- Distinguish requirements for soldering through hole components
- Categorize SMT components
- Identify requirements for surface mount connections
Description:
- Identify general cleanliness requirements
- Describe cleanliness designator
- Differentiate delamination, blistering, conductor separation, lifted lands, measles, and depanelization requirements
- Identify requirements for conformal coating, encapsulation, and staking
Soldering for Electronics Assembly: Introduction

Course Description
To provide learners with an understanding of the soldering process, the role it plays in electronics assembly, and the practical skills required in creating reliable solder connections.
Course Objective
After successfully completing this course, participants/ operators will be able to:
- Identify common features and components of a printed circuit board assembly
- Identify the tools and equipment utilized for soldering
- Practice soldering components onto a printed circuit board
- Build a functional printed circuit board assembly
Description:
- Describe the characteristics of rigid, flex and ceramic PCBs
- Describe the characteristics and function of traces, lands, through-holes, vias, markings, and solder mask
- Explain how soldering is used to connect components to a PCB
Description:
- Describe the composition of the most common types of solder
- Describe the characteristics of eutectic solder
- Distinguish leaded from non-leaded solder
- Identify the different forms of solder
- Select the correct solder wire diameter for a given connection
- Describe the types and function of flux
- Use flux to clean connections and solder iron tips
- Describe the role of heat in the soldering process
Description:
- Identify the parts of a solder station
- Set the temperature on a solder station
- Identify different types of solder tips
- Select the correct size of solder tip
- Use sponge and brass pad to clean a solder tip
- Use solder sick to remove solder
- Use cutters to trim component leads
- Select the correct type of pliers to form component leads
- Explain the function of brushes, tweezers, wooden sticks, and dental picks
- Identify different types of magnification aides
- Set up and use a microscope
Description:
- Explain the process of manually preparing a through-hole component
- Use pliers to form the leads of a through-hole component
- Use cutters to trim the leads of a through-hole component
Description:
- Tin a solder iron tip
- List the steps of the manual soldering process
- Solder through-hole components to a PCB
Description:
- Describe wetting
- Identify a properly wetted solder connection
- Identify common solder connection defects
Description:
- Identify the equipment, tools, and materials used to create basic solder connections
- List steps for applying solder to empty PCB lands and through-holes
- Describe common errors in the soldering process for empty PCB lands and through-holes
- Apply solder to empty PCB lands and through-holes
- List steps for soldering through-hole components to a PCB
- Describe common errors in the through-hole component soldering process
- Solder through-hole components to a PCB
- List steps for soldering chip components to a PCB
- Describe common errors in the chip component soldering process
- Solder chip components to a PCB
- List steps for soldering gull wing components to a PCB
- Describe common errors in the gull wing component soldering process
- Solder gull wing components to a PCB
- Explain two different methods for reworking nonconforming solder connections
INTERNSHIP PROGRAM
Internship Program is designed for youths looking to expand to technical career pathways that help in bridging the gap between academia and the industry need.
Internship seeks to engage students pursuing Engineering Degrees or are Research Scholars enrolled in recognized University/Institution within Gujarat, Bangalore and USA as ‘interns’.
‘Interns’ shall be given exposure to various Verticals/Divisions/Units within “Aimtron” and would be expected to supplement the process of analysis within Aimtron through empirical collection and collation of in-house and other information.
Aimtron technologies opens up Internship Program, for engineering students or research scholars enrolled in recognized universities/institutions in Gujarat, Bangalore and USA.
P.S: Internship duration is as per college requirements, 2weeks, 4 weeks, 6 months and 1 year. Monday-Friday 10am to 5pm.
Registration Form – Apply Here
For technical issues relating to submissions online, please contact csr@aimtron.com.
Read more about Aimtron’s internship:
Download Guidelines Click Here
INDUSTRIAL VISIT
Industrial tour provides students a practical perspective of the work place, working methods and employment practices.
It gives exposure to current work practices as opposed to possibly theoretical knowledge being taught at institute.
Industrial tours provide an excellent opportunity to interact with industries and know more about industrial environment.
Welcome to : Aimtron Technologies Pvt. Ltd.| 1/A, G.I.D.C. Waghodia – 391760 Vadodara(India).
Registration Form – Apply Here
WEBINAR SERIES
Aim of these Webinars is to guide and help students to understand industry’s need and what industry is looking from engineering students.
Webinars are conducted by Industry SMEs and Veterans. This will help you prepare to focus on the domains that you are interested in. You get to know the latest in the Industry and the growth in the industry.
-
- 3. Basics of synthesis & Timing Constraints
- 4. Many more…
If you are having difficulty filling out this form, please contact us.
For India:
Name: Sahana Hegde (Director-Skill development)
Email: csr@aimtron.com
Contact No: (+91) 7041735557
For USA:
Name: Nishtha Vasani (HR Management)
Email: nishtha@aimtron.com
Contact No: (+1) 224-688-0372

















